React 学习笔记
01-创建项目和目录结构
创建项目
- 使用官方脚手架,只做了 react 的基础的搭建和构建,没有路由和全局状态管理,使用 webpack 构建。
npx create-react-app <projectName>npx create-react-app <projectName>- 使用一些第三方集成脚手架,例如典型的 umi ,这一类脚手架创建的项目集成了很多功能,路由、mock 等。
目录结构
react-demo
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ ├── index.html // 挂载app组件
│ ├── logo192.png
│ ├── logo512.png
│ ├── manifest.json
│ └── robots.txt
├── src
│ ├── App.css // APP 样式
│ ├── App.js // App 组件
│ ├── App.test.js // 单元测试(普通项目无需)
│ ├── index.css //全局样式
│ ├── index.js // 入口文件(把项目挂载至指定的dom)
│ ├── logo.svg
│ ├── reportWebVitals.js // 性能报告文件(普通项目无需)
│ └── setupTests.js // 单元测试启动文件(普通项目无需)
├── README.md
├── package-lock.json
└── package.jsonreact-demo
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ ├── index.html // 挂载app组件
│ ├── logo192.png
│ ├── logo512.png
│ ├── manifest.json
│ └── robots.txt
├── src
│ ├── App.css // APP 样式
│ ├── App.js // App 组件
│ ├── App.test.js // 单元测试(普通项目无需)
│ ├── index.css //全局样式
│ ├── index.js // 入口文件(把项目挂载至指定的dom)
│ ├── logo.svg
│ ├── reportWebVitals.js // 性能报告文件(普通项目无需)
│ └── setupTests.js // 单元测试启动文件(普通项目无需)
├── README.md
├── package-lock.json
└── package.json入口文件 - index.js
...
/*
相当于vue中的 main.js - 把项目挂载至指定的dom
vue是创建根实例-通过实例自身app.mount('#app') 挂载至指定的dom
react没有跟实例,根也只是一个组件、后续所有组件都是app的子组件
react-dom 是把一个react组件从一个真正的dom卸载,或者渲染真正的dom
*/
// - 渲染
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
// - 卸载
setTimeout(() => {
root.unmount()
}, 2000)
......
/*
相当于vue中的 main.js - 把项目挂载至指定的dom
vue是创建根实例-通过实例自身app.mount('#app') 挂载至指定的dom
react没有跟实例,根也只是一个组件、后续所有组件都是app的子组件
react-dom 是把一个react组件从一个真正的dom卸载,或者渲染真正的dom
*/
// - 渲染
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
// - 卸载
setTimeout(() => {
root.unmount()
}, 2000)
...对比总结
- vue 是创建根实例,通过调用实例自身
app.mount('#app')方法,挂载至指定的 dom - react 没有创建根实例,通过引入 react-dom 来渲染和挂载指定的 dom。
02-React 组件和 Jsx
组件化开发,定义一个基本组件得有的东西
- 组件 html 模版
- 数据和方法
react 组件的两种写法
函数组件
jsfunction Hello() { return <div>hello</div>; }function Hello() { return <div>hello</div>; }class 组件
jsclass Hello extends React.component { render() { return <div>hello</div>; } }class Hello extends React.component { render() { return <div>hello</div>; } }demo - app.js
import "./App.css";
import React from "react"; // 引入
function App() {
// 与新版本vue3组合式api相似
// 函数组件,编写组件的方法首字母必须大写
function FnHello() {
return <div>hello</div>;
}
// 与老版本vue2选项式api相似
// 类组件,继承React.Component,需要引入 react
class ClassHello extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>hello</div>;
}
}
// 函数式本身就是个方法,返回createElement对象
const obj = FnHello();
console.log(obj);
console.log(<FnHello></FnHello>); // jsx中会识别并编译成Dom对象
return (
<div className="App">
<FnHello></FnHello>
<ClassHello></ClassHello>
</div>
);
}import "./App.css";
import React from "react"; // 引入
function App() {
// 与新版本vue3组合式api相似
// 函数组件,编写组件的方法首字母必须大写
function FnHello() {
return <div>hello</div>;
}
// 与老版本vue2选项式api相似
// 类组件,继承React.Component,需要引入 react
class ClassHello extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>hello</div>;
}
}
// 函数式本身就是个方法,返回createElement对象
const obj = FnHello();
console.log(obj);
console.log(<FnHello></FnHello>); // jsx中会识别并编译成Dom对象
return (
<div className="App">
<FnHello></FnHello>
<ClassHello></ClassHello>
</div>
);
}react 与 jsx 的关系
- react 与 jsx 是相互独立的,vue 中也能是用 jsx
- 使用 jsx 能够在 js 中更方便地编写 html 模版,通过
babel编译转化为 react-createElement 对象 - 如果不借助 jsx,也可直接是用
react.createElement()方法创建 - react 解析对象,创建成页面组件
jsx 里面渲染不同的内容区别
- 字符串,数字:直接渲染
- 对象:只能渲染 element 对象
- { {a: 1} }, 会报错提示:
Objects are not valid as a React child
- { {a: 1} }, 会报错提示:
- 数组:把数组里面每一项单独渲染
- [FnHello(), 1, 2],会报红提示:
Each child in a list should have a unique "key" prop
- [FnHello(), 1, 2],会报红提示:
- 表达式:运行表达式
- 方法: 无法渲染
- 布尔值:不渲染任何内容
- undefined、null:不渲染任何内容
总结
- react 的两种组件,函数式组件、class 类组件,分别与 vue3 的组合式 api 和 vue2 的选项式 api 相似
- 注意的点:编写函数组件必须首字母大写
- vue 有 vue 文件的编译模版,react 是同过借助 jsx 语法来编写 html 模版
- jsx 不像 vue 模版,vue 模版会把本身编译为字符串显示出来,像变量方法布尔、undefined、null 会显示出对应的字符串
待补充:函数组件与 class 组件的差异、vue2\vue3
- vue3 可以按需引入,减小的打包体积
03-React 的事件绑定
规则模式
- 与原生相似,on+事件名(只不过首字母要大写)
- on+事件后面接收的必须是一个方法
特别注意的点
- 不做任何处理的情况下,this 会指向 undefined
- 给到事件绑定的一定是一个方法 fn,不能直接调用 fn(),调用方法只会在初次渲染页面时执行一次。
function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>点击按钮</div> // undefined
</div>
}function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>点击按钮</div> // undefined
</div>
}解决方案
- 给方法调用 bind 规定 this
function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>点击按钮</div> // undefined
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>点击按钮</div> // undefined
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}- 写成一个匿名箭头函数
function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={() => {
console.log(this); // Test1
}}
>点击</div>
</div>
}function handleClick() {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={() => {
console.log(this); // Test1
}}
>点击</div>
</div>
}- 方法本身写成箭头函数
function handleClick() {}[!code --]
handleClick = () => {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
<div onClick={this.handleClick(this)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}function handleClick() {}[!code --]
handleClick = () => {}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
<div onClick={this.handleClick(this)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}事件绑定其他操作
- 传递参数
- 获取事件对象
- 阻止默认行为,冒泡等
// 通过.bind()传递参数
handleClick = (a, b, event) => {
// event并不是原生的,是合成的,使用上跟原生相似 is+原生方法名
// event.stopPropagation() 原生
console.log(event.isDefaultPrevented()) // 阻止默认行为,冒泡等
console.log(a + b, event);
};
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this, 1, 2)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}// 通过.bind()传递参数
handleClick = (a, b, event) => {
// event并不是原生的,是合成的,使用上跟原生相似 is+原生方法名
// event.stopPropagation() 原生
console.log(event.isDefaultPrevented()) // 阻止默认行为,冒泡等
console.log(a + b, event);
};
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>点击按钮</div>
<div onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this, 1, 2)}>点击按钮</div>
</div>
}总结
- jsx 中单花括号{ }中接收一个方法 fn,不能直接调用 fn()
- this 指向问题,默认 undefined,通过箭头函数、.bind(this)可解决,推荐使用 bind 方便传参数
- 事件对象为最后一个参数,只不过这个事件对象是复合的,里面属性 nativeXXX 是原生
- 复合的事件对象调用阻止默认行为:e.is+方法名,与原生:e.方法名有点不同
04-React 的响应式数据
流程
state 中定义变量 -> 通过调佣 setState给入一个对象 -> setState将给入的对象和state对象进行浅合并 -> 统一触发更新
关键点:
- 只合并第一层,会将对应键值直接顶替
- 调用
setState触发更新,直接修改state不会触发
class Test04 extends React.Component {
// constructor(props) {
// super(props);
// this.state = {
// a: 1,
// };
// }
// 忽略constructor,使用ES7写法
state = {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
bodyInfo: {
height: 172,
weight: 60,
},
likes: ["游泳、", "跑步、", "篮球"],
};
add = () => {
// 1.修改值,单独触发更新
// this.state.a += 1;
// this.setState({});
//2. 修改值并触发跟新
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1,
bodyInfo: {
// 该对象将覆盖原来的值
height: this.state.bodyInfo.height + 1,
// weight: 60, // 注释该行,体重信息就不展示了
},
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>姓名: {this.state.name}</div>
<div>年龄:{this.state.age}</div>
<div>
身体状况:身高:{this.state.bodyInfo.height} | 体重: {this.state.bodyInfo.weight}
</div>
<button onClick={this.add}>年龄\身高加1</button>
</div>
);
}
}class Test04 extends React.Component {
// constructor(props) {
// super(props);
// this.state = {
// a: 1,
// };
// }
// 忽略constructor,使用ES7写法
state = {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
bodyInfo: {
height: 172,
weight: 60,
},
likes: ["游泳、", "跑步、", "篮球"],
};
add = () => {
// 1.修改值,单独触发更新
// this.state.a += 1;
// this.setState({});
//2. 修改值并触发跟新
this.setState({
age: this.state.age + 1,
bodyInfo: {
// 该对象将覆盖原来的值
height: this.state.bodyInfo.height + 1,
// weight: 60, // 注释该行,体重信息就不展示了
},
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>姓名: {this.state.name}</div>
<div>年龄:{this.state.age}</div>
<div>
身体状况:身高:{this.state.bodyInfo.height} | 体重: {this.state.bodyInfo.weight}
</div>
<button onClick={this.add}>年龄\身高加1</button>
</div>
);
}
}setState 异步 or 同步
setState 是异步的,想要同步得到修改后的结果,可以在第二个参数传入一个回调函数,在这个函数中获取
// ...
this.setState(
{
age: this.state.age + 1,
bodyInfo: {
// 该对象将覆盖原来的值
height: this.state.bodyInfo.height + 1,
// weight: 60, // 注释该行,体重信息就不展示了
},
},
() => {
console.log(this.state.age); // 19
}
);
console.log(this.state.age); // 18
// ...// ...
this.setState(
{
age: this.state.age + 1,
bodyInfo: {
// 该对象将覆盖原来的值
height: this.state.bodyInfo.height + 1,
// weight: 60, // 注释该行,体重信息就不展示了
},
},
() => {
console.log(this.state.age); // 19
}
);
console.log(this.state.age); // 18
// ...关于多次调用 setState
- setState 多个修改,会合并为一次,再统一更新
this.setState({
name: "李明花",
});
this.setState({
age: 20,
});
// 相当于
this.setState({
name: "李明花",
age: 20,
});this.setState({
name: "李明花",
});
this.setState({
age: 20,
});
// 相当于
this.setState({
name: "李明花",
age: 20,
});setState返回会触发更新render(),不管你有没有修改,这造成了一个问题,重复修改为相同的值也会让组件更新
- 解决方案: 使用
React.PureComponent
class Test04 extends React.Component {
class Test04 extends React.PureComponent {
// ...
changeAge = () => {
this.setState({
age: 20
})
}
render() {
console.log('render') // 只在第一次渲染和第一次更新触发
return <div>
<button onClick={this.changeAge.bind(this)}>年龄改为20</button>
</div>
}
}class Test04 extends React.Component {
class Test04 extends React.PureComponent {
// ...
changeAge = () => {
this.setState({
age: 20
})
}
render() {
console.log('render') // 只在第一次渲染和第一次更新触发
return <div>
<button onClick={this.changeAge.bind(this)}>年龄改为20</button>
</div>
}
}PureComponent判断数组和对象方式:内存地址引用是否发生改变
// ...
// 修改对象
changeBodyInfo = () => {
this.setState({
bodyInfo: this.state.bodyInfo, // 不会触发更新
bodyInfo: {...this.state.bodyInfo}, // 触发一次
});
}
// 修改数组
changeLikes = () => {
this.setState({
likes: this.state.likes, // 不会触发更新
likes: [...this.state.likes],
});
};
render() {
console.log('render')
return <div>
<div>
身体状况:身高:{this.state.bodyInfo.height} | 体重: {this.state.bodyInfo.weight}
</div>
<div>爱好: {this.state.likes}</div>
<button onClick={this.changeBodyInfo.bind(this)}>身体情况保持不变</button>
<button onClick={this.changeLikes.bind(this)}>爱好保持不变</button>
</div>
}
// ...// ...
// 修改对象
changeBodyInfo = () => {
this.setState({
bodyInfo: this.state.bodyInfo, // 不会触发更新
bodyInfo: {...this.state.bodyInfo}, // 触发一次
});
}
// 修改数组
changeLikes = () => {
this.setState({
likes: this.state.likes, // 不会触发更新
likes: [...this.state.likes],
});
};
render() {
console.log('render')
return <div>
<div>
身体状况:身高:{this.state.bodyInfo.height} | 体重: {this.state.bodyInfo.weight}
</div>
<div>爱好: {this.state.likes}</div>
<button onClick={this.changeBodyInfo.bind(this)}>身体情况保持不变</button>
<button onClick={this.changeLikes.bind(this)}>爱好保持不变</button>
</div>
}
// ...- 一定不要在
render里直接setState,否则死机。。
总结
- 在
state中定义变量,通过setState({})触发页面更新 setState可以做两件事,修改state里的值,触发render()- 多次调用会先合并,再统一修改
setState()为异步,想要拿到更新后的值,可以在第二个参数回调函数中获取- 页面操作触发
setState去改变的值结果都是不变的,也会造成重新 render 问题 - 使用
React.PureComponent,假如setState的值结果没有发生改变,则不会触发更新 PureComponent中判断值是否改变,是判断内存地址的引用,数组和对象必须赋予一个新的数组对象- 避免操作原数据,先拷贝一份,在拷贝数据上进行操作,之后再赋予
05-条件渲染和列表循环
条件渲染
原则:
- react 渲染 undefined、null、空字符串、false、不会渲染任何内容
- 如果渲染一个 jsx 编写的 html 元素,就会渲染成页面上的内容
只需运用逻辑运算,true 返回一个 html 元素结构;false 返回个空字符串就不会显示任何内容
// ...
class Test05 extends PureComponent {
state = {
isShow: true, // 定义一个控制显示隐藏变量
};
// 判断是/否显示div
fn1 = () => {
if (this.state.isShow) {
return <div>div</div>;
} else {
return "";
}
};
// 切换显示/隐藏
handleIsShow = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: !this.state.isShow,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>条件渲染</div>
{this.fn1()}
{/* {this.state.isShow ? <div>显示</div> : ""} */}
<button onClick={this.handleIsShow}>{this.state.isShow ? "隐藏" : "显示"}</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// ...// ...
class Test05 extends PureComponent {
state = {
isShow: true, // 定义一个控制显示隐藏变量
};
// 判断是/否显示div
fn1 = () => {
if (this.state.isShow) {
return <div>div</div>;
} else {
return "";
}
};
// 切换显示/隐藏
handleIsShow = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: !this.state.isShow,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>条件渲染</div>
{this.fn1()}
{/* {this.state.isShow ? <div>显示</div> : ""} */}
<button onClick={this.handleIsShow}>{this.state.isShow ? "隐藏" : "显示"}</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// ...列表循环
原则
- 渲染一个数组会把数组里面的每一项单独取出渲染
- 那么我们编写一个里面存放的都是 html 结构的数组,就会渲染成页面上的列表
通过循环原始数据,把原始数据生成为一个存放列表每一项元素的新数组,jsx 编译存着 html 结构的数组,在页面上渲染为列表
// ...
class Test05 extends PureComponent {
state = {
originArr: [1, 2, 3], // 转为[<div>1</div>, <div>2</div>, <div>3</div>]
};
// 处理新数组
getArr = () => {
// 工作中常用 map、filter来实现
let newArr = [];
this.state.originArr.forEach((item) => {
newArr.push(<div key={item}>{item}</div>);
});
return newArr;
};
// 添加数组数据
handleArrPush = () => {
let newArr = [...this.state.originArr];
const len = this.state.originArr.length + 1;
newArr.push(len);
this.setState({
originArr: newArr,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>列表循环</div>
{/* {this.getArr()} */}
{this.state.originArr.map((item) => {
return <div key={item}>{item}</div>;
})}
<button onClick={this.handleArrPush}>添加数组数据</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// ...// ...
class Test05 extends PureComponent {
state = {
originArr: [1, 2, 3], // 转为[<div>1</div>, <div>2</div>, <div>3</div>]
};
// 处理新数组
getArr = () => {
// 工作中常用 map、filter来实现
let newArr = [];
this.state.originArr.forEach((item) => {
newArr.push(<div key={item}>{item}</div>);
});
return newArr;
};
// 添加数组数据
handleArrPush = () => {
let newArr = [...this.state.originArr];
const len = this.state.originArr.length + 1;
newArr.push(len);
this.setState({
originArr: newArr,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>列表循环</div>
{/* {this.getArr()} */}
{this.state.originArr.map((item) => {
return <div key={item}>{item}</div>;
})}
<button onClick={this.handleArrPush}>添加数组数据</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// ...总结
- 纯粹的 js 逻辑运算,灵活、自由度高,注意的点:避免操作原数据
- 不像 vue 有 v-show、v-if、v-for 指令,使用起来方便、但也受限制
06-表单绑定
基本思路
React 中很多思路都是按原生的操作去做的,表单绑定也是如此。
原生表单获取表单输入值,可以通过监听input、change等事件,然后获取e.target.value
如果要设置表单的值,通常设置value属性,如果是选择框则是checked属性
受控组件与非受控组件
- 非受控组件: 数据单向绑定,使用者只能获取它的值,值只能表单自身去修改,也就就只做了监
// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.state.inputValue}
<input
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value,
});
}}
></input>
</div>
);
}
}
//...// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.state.inputValue}
<input
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value,
});
}}
></input>
</div>
);
}
}
//...- 受控组件:数据双向绑定,表单的值可以由使用者通过修改 state 数据,影响表单显示的值
// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
};
handleChangeInputValue = () => {
this.setState({
inputValue: "王花花",
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.state.inputValue}
<input
// 通过设置value实现双向绑定
value={this.state.inputValue}
// 通过监听input事件获取并保存value值
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value,
});
}}
></input>
{/* 手动设置表单的值 */}
<button onClick={this.handleChangeInputValue}>改变输入框的值</button>
</div>
);
}
}
//...// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
};
handleChangeInputValue = () => {
this.setState({
inputValue: "王花花",
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.state.inputValue}
<input
// 通过设置value实现双向绑定
value={this.state.inputValue}
// 通过监听input事件获取并保存value值
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value,
});
}}
></input>
{/* 手动设置表单的值 */}
<button onClick={this.handleChangeInputValue}>改变输入框的值</button>
</div>
);
}
}
//...原生多选框实现双向绑定
// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
checkList: [],
};
// 处理多选框
handleChangeChecked = (e) => {
let arr = [...this.state.checkList];
if (e.target.checked) {
arr.push(e.target.value);
} else {
arr.splice(arr.indexOf(e.target.value), 1);
}
this.setState({
checkList: arr,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>---------------------</div>
{this.state.checkList}
<div>---------------------</div>
{/* 设置每个选中获取的值(value),通过checked控制是否选中 */}
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c1")} value="c1" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项一
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c2")} value="c2" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项二
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c3")} value="c3" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项三
</div>
);
}
}
//...// ...
class Test06 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
checkList: [],
};
// 处理多选框
handleChangeChecked = (e) => {
let arr = [...this.state.checkList];
if (e.target.checked) {
arr.push(e.target.value);
} else {
arr.splice(arr.indexOf(e.target.value), 1);
}
this.setState({
checkList: arr,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div>---------------------</div>
{this.state.checkList}
<div>---------------------</div>
{/* 设置每个选中获取的值(value),通过checked控制是否选中 */}
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c1")} value="c1" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项一
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c2")} value="c2" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项二
<input checked={this.state.checkList.includes("c3")} value="c3" type="checkbox" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChangeChecked} />
选项三
</div>
);
}
}
//...总结
- 获取:基本跟原生一样,通过监听 input、change 事件来获取 e.target.value 值
- 修改:通过设置 value 或 checked 来改变表单的值
- 输入框、单选操作多数绑定一个字符串或者布尔值,多选操作绑定数组,这两点实现方式有些许不一样。
- 单向绑定成为非受控组件
- 双向绑定称为受控组件
07-Props 和组件间的传值、插槽
props 是 react 的核心
在 react 中,所有卸载组件上的属性和子节点都被规划为 props。
所以 props 是 react 很多功能的根本。父子传值,插槽全都是基于 props,不像 vue 定义 props 字段才作为 props,事件监听、emit,专门的插槽这一类东西。
传值(父传子)
- 获取:上级组件绑定属性
msg={},子级组件通过this.props.msg获取 - 校验:组件.propTypes,设置字段并赋予一个函数,获取参数 props 自定义校验逻辑,也可引入 react 的 propTypes 类型校验
- 默认值:组件.defaultProps,设置字段并赋予默认值
import React from "react";
import propTypes from "prop-types";
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
sonMsg: "this value from son",
};
render() {
// 通过 this.props获取字段值
return (
<div className="container">
<div> {this.props.msg}</div>
<div>{this.state.sonMsg}</div>I am son components.
</div>
);
}
}
// 类型校验
Test07.propTypes = {
// msg: function (props) {
// if (typeof props.msg !== "string") {
// throw new Error("msg must be a string");
// }
// },
msg: propTypes.string,
};
// 默认值
Test07.defaultProps = {
msg: "I am default msg",
};
export default Test07;import React from "react";
import propTypes from "prop-types";
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
sonMsg: "this value from son",
};
render() {
// 通过 this.props获取字段值
return (
<div className="container">
<div> {this.props.msg}</div>
<div>{this.state.sonMsg}</div>I am son components.
</div>
);
}
}
// 类型校验
Test07.propTypes = {
// msg: function (props) {
// if (typeof props.msg !== "string") {
// throw new Error("msg must be a string");
// }
// },
msg: propTypes.string,
};
// 默认值
Test07.defaultProps = {
msg: "I am default msg",
};
export default Test07;// ...
import Test07 from "./components/07-props和组件间传值和插槽";
function App() {
const state = {
msg: false
}
return (
<div className="App">
<Test07 msg={state.msg}></Test07>
</div>
);// ...
import Test07 from "./components/07-props和组件间传值和插槽";
function App() {
const state = {
msg: false
}
return (
<div className="App">
<Test07 msg={state.msg}></Test07>
</div>
);插槽
- 默认插槽
- 具名插槽
- 作用域插槽
import React from "react";
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
scopeSlotValue: "scope slot",
};
render() {
// 通过 this.props获取字段值
return (
<div className="container">
{/* 默认插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.children}</div>
{/* 具名插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.slotA}</div>
{/* 作用域插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.scopeSlot(this.state.scopeSlotValue)}</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Test07;import React from "react";
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
scopeSlotValue: "scope slot",
};
render() {
// 通过 this.props获取字段值
return (
<div className="container">
{/* 默认插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.children}</div>
{/* 具名插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.slotA}</div>
{/* 作用域插槽 */}
<div>{this.props.scopeSlot(this.state.scopeSlotValue)}</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Test07;// ...
import Test07 from "./components/07-props和组件间传值和插槽";
function App() {
const state = {
msg: false
}
return (
<div className="App">
<Test07
msg={state.msg}
slotA={<div>slotA</div>}
scopeSlot={(scope) => {
return <div>{scope}</div>;
}}
>
<div>default slot</div>
</Test07>
</div>
);// ...
import Test07 from "./components/07-props和组件间传值和插槽";
function App() {
const state = {
msg: false
}
return (
<div className="App">
<Test07
msg={state.msg}
slotA={<div>slotA</div>}
scopeSlot={(scope) => {
return <div>{scope}</div>;
}}
>
<div>default slot</div>
</Test07>
</div>
);传值(子传父)
- 父组件把方法传递给子组件
- 子组件调用传递过来的方法
- 调用时传递参数
- 父组件执行方法,进行操作,注意 this 指向问题
// 这里使用Class组件演示,函数组件触发更新需要借助hook,后面学习到再用
class AppClass extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "this value from parent",
};
changeMsg(value) {
// console.log(this)
// 没有使用bind(this)改变或箭头函数的话,指向子组件中的props
this.setState({
msg: value,
});
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 传值给子组件 */}
<Test07
msg={this.state.msg}
/* 获取子组件传过来的值,通过子组件调用修改msg值 */
changeMsg={this.changeMsg.bind(this)}
>
<div>default slot</div>
</Test07>
</div>
);
}
}// 这里使用Class组件演示,函数组件触发更新需要借助hook,后面学习到再用
class AppClass extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "this value from parent",
};
changeMsg(value) {
// console.log(this)
// 没有使用bind(this)改变或箭头函数的话,指向子组件中的props
this.setState({
msg: value,
});
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 传值给子组件 */}
<Test07
msg={this.state.msg}
/* 获取子组件传过来的值,通过子组件调用修改msg值 */
changeMsg={this.changeMsg.bind(this)}
>
<div>default slot</div>
</Test07>
</div>
);
}
}//...
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.props.msg}
{/* 调用父组件方法,给父组件传值 */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.changeMsg("hello");
}}
>
给父组件传值
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
//...//...
class Test07 extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
{this.props.msg}
{/* 调用父组件方法,给父组件传值 */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.changeMsg("hello");
}}
>
给父组件传值
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
//...兄弟组件传值
- 子 1 -> 父组件 -> 子 2
// ...
import SonA from "./SonA";
import SonB from "./SonB";
class AppClass extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "this value from parent",
};
getMsg = (value) => {
this.setState({
msg: value,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 兄弟组件通过父组件传值 */}
<SonA getMsg={this.getMsg}></SonA>
<SonB sonAMsg={this.state.msg}></SonB>
</div>
);
}
}
//...// ...
import SonA from "./SonA";
import SonB from "./SonB";
class AppClass extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "this value from parent",
};
getMsg = (value) => {
this.setState({
msg: value,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 兄弟组件通过父组件传值 */}
<SonA getMsg={this.getMsg}></SonA>
<SonB sonAMsg={this.state.msg}></SonB>
</div>
);
}
}
//...class SonA extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
msg: "I am sonA",
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
SonA
{/* 点击调用父组件方法传递msg,父组件保存msg并通过props传给SonB */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.getMsg(this.state.msg);
}}
>
点击给SonB传值
</button>
</div>
);
}
}class SonA extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
msg: "I am sonA",
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
SonA
{/* 点击调用父组件方法传递msg,父组件保存msg并通过props传给SonB */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.getMsg(this.state.msg);
}}
>
点击给SonB传值
</button>
</div>
);
}
}class SonB extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
return <div className="container">SonB:获取SonA的msg为“{this.props.sonAMsg}”</div>;
}
}class SonB extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
return <div className="container">SonB:获取SonA的msg为“{this.props.sonAMsg}”</div>;
}
}- eventBus(空)
总结
- 统统通过 props 实现
- 父传子要数据传数据,要插槽传 html 模版结构
- 子传父通过传递函数,子组件调用并传递参数
- 兄弟组件可通过父组件作为媒介进行传递 or 写个 eventBus
08-React 中的样式操作
- className 类名必须接收一个字符串
- style 内联样式必须接收一个对象
import React from "react";
import Son from "./Son.js";
import "./App.css"; // 作用于全局,就算再外层使用了该文件内的类名样式,照样生效
class Test08 extends React.Component {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="father" style={{ color: "#fff", fontWeight: 700 }}>
father
<Son></Son>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Test08;import React from "react";
import Son from "./Son.js";
import "./App.css"; // 作用于全局,就算再外层使用了该文件内的类名样式,照样生效
class Test08 extends React.Component {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="father" style={{ color: "#fff", fontWeight: 700 }}>
father
<Son></Son>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Test08;import React from "react";
// import "./Son.css";
// import classnames from "classnames/bind"
// 如果引入引入模块,要引入classnames中的bind文件夹
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
// import classnames from "classnames/bind"
class Son extends React.Component {
state = {
hasSon1: true
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className={sonStyle.son}> Son</div>
{/* <div
className={classnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1,
})}
>
Son
</div> */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({
hasSon1: true,
});
}}
>
覆盖
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({
hasSon1: false,
});
}}
>
移除
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;import React from "react";
// import "./Son.css";
// import classnames from "classnames/bind"
// 如果引入引入模块,要引入classnames中的bind文件夹
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
// import classnames from "classnames/bind"
class Son extends React.Component {
state = {
hasSon1: true
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className={sonStyle.son}> Son</div>
{/* <div
className={classnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1,
})}
>
Son
</div> */}
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({
hasSon1: true,
});
}}
>
覆盖
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({
hasSon1: false,
});
}}
>
移除
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;.father {
background-color: blueviolet;
}.father {
background-color: blueviolet;
}.son {
background-color: brown;
}.son {
background-color: brown;
}针对组件内部生效的 css 样式
- 使用 css 模块化
import React from "react";
import "./Son.css";
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
console.log(sonStyle); // {son: 'Son_son__g33Pp', son1: 'Son_son1__e7hIv'}
// vue <style scope>
// react xxx.module.css
class Son extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="son"> Son</div>
<div className={sonStyle.son}> Son</div>;
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;import React from "react";
import "./Son.css";
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
console.log(sonStyle); // {son: 'Son_son__g33Pp', son1: 'Son_son1__e7hIv'}
// vue <style scope>
// react xxx.module.css
class Son extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="son"> Son</div>
<div className={sonStyle.son}> Son</div>;
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;.son {
background-color: pink;
}
.son1 {
background-color: green;
}.son {
background-color: pink;
}
.son1 {
background-color: green;
}优雅控制类名的添加减少
- 使用 classnames 第三方库
npm install classnamesnpm install classnames//..
import "./Son.css";
import classnames from "classnames/bind";
let str = classnames({
son: true,
son1: true,
});
state = {
hasSon1: true,
};
class Son extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div
className={classnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1,
})}
>
Son
</div>
<button></button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;//..
import "./Son.css";
import classnames from "classnames/bind";
let str = classnames({
son: true,
son1: true,
});
state = {
hasSon1: true,
};
class Son extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div
className={classnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1,
})}
>
Son
</div>
<button></button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;// 如果引入引入模块,要引入classnames中的bind文件夹
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
import classnames from "classnames/bind";
let bindClassnames = classnames.bind(sonStyle);// 如果引入引入模块,要引入classnames中的bind文件夹
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css";
import classnames from "classnames/bind";
let bindClassnames = classnames.bind(sonStyle);总结
- className 接收字符串,style 接收对象
- 内部样式隔离使用 css 模块化实现
- 动态样式借助第三方库 classnames 优化写法
09-生命周期
三大部分(挂载、更新、卸载)、两大阶段(render、commit)
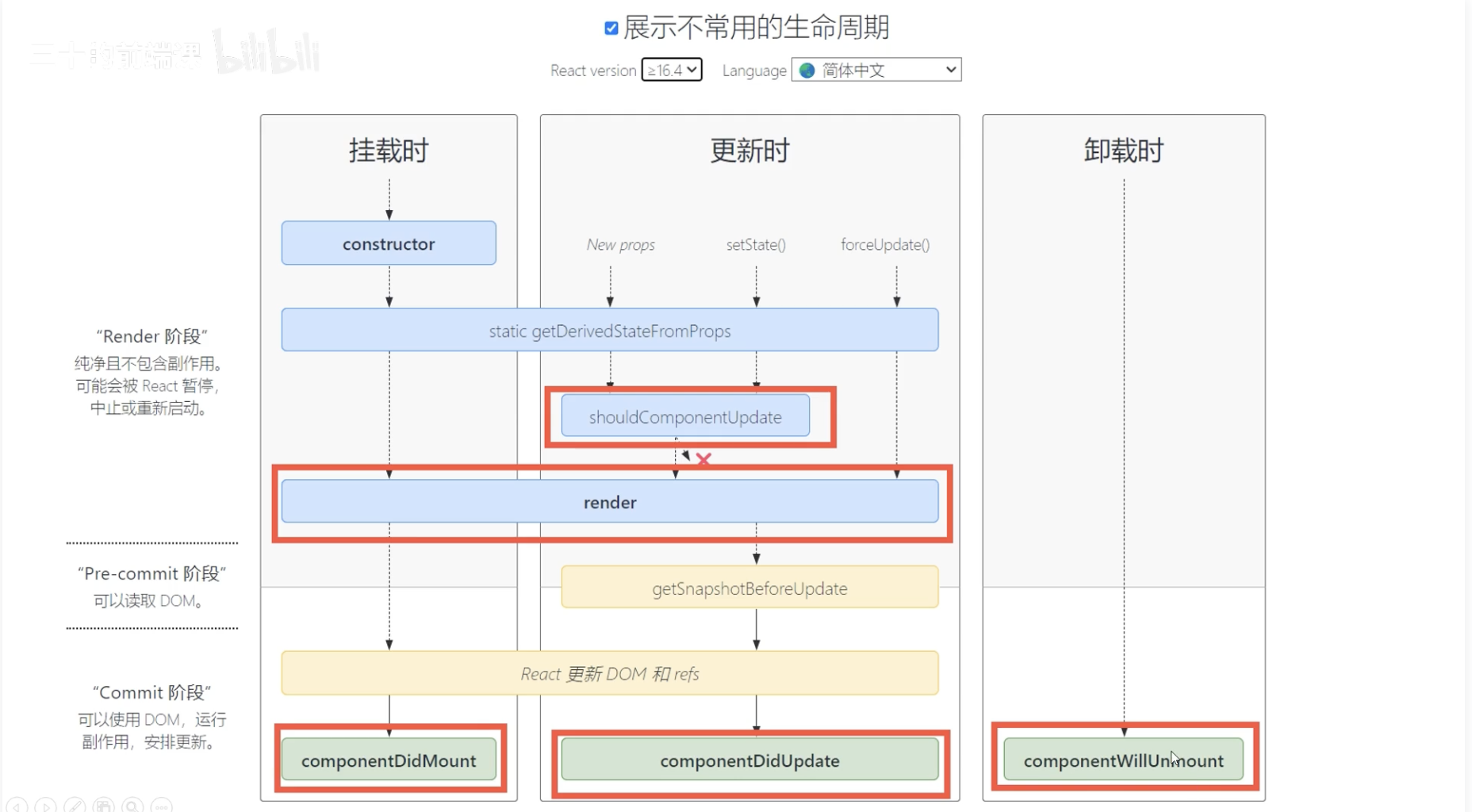
重点钩子
render, 通过 render 函数的执行来决定组件渲染的内容,所以无论更新还是初次挂载都会执行。componentDidMount,组件过载完成,一般用来做一些页面初始化操作,比如初始请求,echarts 绘制等,也就是 vue 的 mounted 里做的事一样。shouldComponentUpdate,更新阶段调用,如果 return false 则不会执行 render 函数继续更新,从而达到阻止更新的效果,一般用来做性能优化。componentDidUpdate,更新完成,等同于 vue 的 updatedcomponentWillUnmount,组件卸载,通常做一些全局事件监听、计时器的卸载
相比较 vue,react 更新方案
- vue 是在 get 和 set 里触发更新,vue 在 get 中有一个重要的操作-依赖收集,这样我们在修改数据时,只会更新用到了这个数据的地方。做到最小的更新范围。
- react 是通过调用 setState 触发的更新,并没有收集依赖,所以它是整个组件树更新,即使没用到数据的子组件也会一块更新。
严格模式 <React.strictMode>
严格模式只在开发模式下生效,生产上线时会去除,作用简要概括有两方面的作用:
- 检测一些危险操作,比如使用已经作废 api 和不推荐的 api
- 会把一些生命周期执行两次,来检测额外副作用,比如 render
10-实战编写增删改查列表
import React from "react";
import propTypes from "prop-types";
import modelStyle from "./Model.module.css";
class Model extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div className={modelStyle.cover}>
<div className={modelStyle.content}>
{/* <div className={modelStyle.title}>{this.props.title ? this.props.title : "标题"}</div> */}
<div className={modelStyle.title}>{this.props.title}</div>
<div>{this.props.children}</div>
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.confirm();
}}
>
确定
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.cancel();
}}
>
取消
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
Model.propsTypes = {
title: propTypes.string,
};
Model.defaultProps = {
title: "新增",
};
export default Model;import React from "react";
import propTypes from "prop-types";
import modelStyle from "./Model.module.css";
class Model extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div className={modelStyle.cover}>
<div className={modelStyle.content}>
{/* <div className={modelStyle.title}>{this.props.title ? this.props.title : "标题"}</div> */}
<div className={modelStyle.title}>{this.props.title}</div>
<div>{this.props.children}</div>
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.confirm();
}}
>
确定
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.props.cancel();
}}
>
取消
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
Model.propsTypes = {
title: propTypes.string,
};
Model.defaultProps = {
title: "新增",
};
export default Model;import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
import Model from "./Model";
const mockData = [
{ id: 1, date: "2023-12-01", name: "订单一", status: 0 },
{ id: 2, date: "2023-12-02", name: "订单二", status: 1 },
{ id: 3, date: "2023-12-03", name: "订单三", status: 2 },
];
const statusMap = [
{ text: "进行中", color: "blue" },
{ text: "已完成", color: "green" },
{ text: "已延期", color: "red" },
];
class SearchTableList extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
isShow: false,
tableList: [],
searchParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
modelParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
};
componentDidMount() {
// 页面挂载请求数据
this.getTableList();
}
// 模拟接口数据
mockAxiosGet = (params = this.state.searchParams) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 目前先支持日期单项查询
if (params.date) {
resolve({
code: 200,
data: mockData.filter((e) => e.date.indexOf(params.date) != -1),
message: "请求成功",
});
} else {
resolve({
code: 200,
data: mockData,
message: "请求成功",
});
}
}, 200);
});
};
// 模拟获取数据
getTableList = () => {
this.mockAxiosGet().then((res) => {
if (res.code == 200) {
this.setState(
{
tableList: [...res.data],
},
() => {
console.log("请求成功,数据为:", res.data);
}
);
} else {
alert("请求失败");
}
});
};
handleDelete = (id) => {
const idx = mockData.findIndex((v) => v.id == id);
mockData.splice(idx, 1);
console.log(mockData);
this.getTableList();
};
handleEdit = (e) => {
this.setState({
isShow: true,
modelParams: { ...e },
});
};
handleAdd = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: true,
});
};
handleConfirm = () => {
if (this.state.modelParams.id) {
mockData.forEach((e, i) => {
if (e.id == this.state.modelParams.id) {
mockData[i] = this.state.modelParams;
}
});
this.getTableList();
} else {
mockData.push({ id: Math.random() * 100, ...this.state.modelParams });
this.getTableList();
}
this.handleCancel();
};
handleCancel = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: false,
modelParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="search-box">
<div>
日期:
<input
value={this.state.searchParams.date}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
date: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
订单名:
<input
value={this.state.searchParams.name}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
name: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
状态:
<select
value={this.state.searchParams.status}
onChange={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
status: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
>
{statusMap.map((item, index) => {
return (
<option key={index} value={index}>
{item.text}
</option>
);
})}
</select>
</div>
<button onClick={this.getTableList}>查询</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState(
{
searchParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
},
() => {
this.getTableList();
}
);
}}
>
重置
</button>
<button onClick={this.handleAdd.bind(this)}>新增</button>
</div>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<td>日期</td>
<td>订单名</td>
<td>订单状态</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.state.tableList.map((item) => {
return (
<tr key={item.id}>
<td>{item.date}</td>
<td>{item.name}</td>
<td
style={{
color: statusMap[item.status].color,
}}
>
{statusMap[item.status].text}
</td>
<td>
<button onClick={this.handleDelete.bind(this, item.id)}>删除</button>
<button onClick={this.handleEdit.bind(this, item)}>编辑</button>
</td>
</tr>
);
})}
</tbody>
</table>
{/* 弹窗 */}
{this.state.isShow ? (
<Model title={this.state.modelParams.id ? "新增" : "编辑"} confirm={this.handleConfirm} cancel={this.handleCancel}>
<div>
日期:
<input
value={this.state.modelParams.date}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
date: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
订单名:
<input
value={this.state.modelParams.name}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
name: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
状态:
<select
value={this.state.modelParams.status}
onChange={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
status: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
>
{statusMap.map((item, index) => {
return (
<option key={index} value={index}>
{item.text}
</option>
);
})}
</select>
</div>
</Model>
) : (
""
)}
</div>
);
}
}
export default SearchTableList;import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
import Model from "./Model";
const mockData = [
{ id: 1, date: "2023-12-01", name: "订单一", status: 0 },
{ id: 2, date: "2023-12-02", name: "订单二", status: 1 },
{ id: 3, date: "2023-12-03", name: "订单三", status: 2 },
];
const statusMap = [
{ text: "进行中", color: "blue" },
{ text: "已完成", color: "green" },
{ text: "已延期", color: "red" },
];
class SearchTableList extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
isShow: false,
tableList: [],
searchParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
modelParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
};
componentDidMount() {
// 页面挂载请求数据
this.getTableList();
}
// 模拟接口数据
mockAxiosGet = (params = this.state.searchParams) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 目前先支持日期单项查询
if (params.date) {
resolve({
code: 200,
data: mockData.filter((e) => e.date.indexOf(params.date) != -1),
message: "请求成功",
});
} else {
resolve({
code: 200,
data: mockData,
message: "请求成功",
});
}
}, 200);
});
};
// 模拟获取数据
getTableList = () => {
this.mockAxiosGet().then((res) => {
if (res.code == 200) {
this.setState(
{
tableList: [...res.data],
},
() => {
console.log("请求成功,数据为:", res.data);
}
);
} else {
alert("请求失败");
}
});
};
handleDelete = (id) => {
const idx = mockData.findIndex((v) => v.id == id);
mockData.splice(idx, 1);
console.log(mockData);
this.getTableList();
};
handleEdit = (e) => {
this.setState({
isShow: true,
modelParams: { ...e },
});
};
handleAdd = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: true,
});
};
handleConfirm = () => {
if (this.state.modelParams.id) {
mockData.forEach((e, i) => {
if (e.id == this.state.modelParams.id) {
mockData[i] = this.state.modelParams;
}
});
this.getTableList();
} else {
mockData.push({ id: Math.random() * 100, ...this.state.modelParams });
this.getTableList();
}
this.handleCancel();
};
handleCancel = () => {
this.setState({
isShow: false,
modelParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
});
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="search-box">
<div>
日期:
<input
value={this.state.searchParams.date}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
date: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
订单名:
<input
value={this.state.searchParams.name}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
name: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
状态:
<select
value={this.state.searchParams.status}
onChange={(e) => {
this.setState({
searchParams: {
...this.state.searchParams,
status: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
>
{statusMap.map((item, index) => {
return (
<option key={index} value={index}>
{item.text}
</option>
);
})}
</select>
</div>
<button onClick={this.getTableList}>查询</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState(
{
searchParams: {
date: "",
name: "",
status: 0,
},
},
() => {
this.getTableList();
}
);
}}
>
重置
</button>
<button onClick={this.handleAdd.bind(this)}>新增</button>
</div>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<td>日期</td>
<td>订单名</td>
<td>订单状态</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.state.tableList.map((item) => {
return (
<tr key={item.id}>
<td>{item.date}</td>
<td>{item.name}</td>
<td
style={{
color: statusMap[item.status].color,
}}
>
{statusMap[item.status].text}
</td>
<td>
<button onClick={this.handleDelete.bind(this, item.id)}>删除</button>
<button onClick={this.handleEdit.bind(this, item)}>编辑</button>
</td>
</tr>
);
})}
</tbody>
</table>
{/* 弹窗 */}
{this.state.isShow ? (
<Model title={this.state.modelParams.id ? "新增" : "编辑"} confirm={this.handleConfirm} cancel={this.handleCancel}>
<div>
日期:
<input
value={this.state.modelParams.date}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
date: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
订单名:
<input
value={this.state.modelParams.name}
onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
name: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
></input>
</div>
<div>
状态:
<select
value={this.state.modelParams.status}
onChange={(e) => {
this.setState({
modelParams: {
...this.state.modelParams,
status: e.target.value,
},
});
}}
>
{statusMap.map((item, index) => {
return (
<option key={index} value={index}>
{item.text}
</option>
);
})}
</select>
</div>
</Model>
) : (
""
)}
</div>
);
}
}
export default SearchTableList;.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
flex-direction: column;
width: 500px;
}
.search-box {
display: flex;
justify-content: start;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
table {
border: 1px solid #333;
}
td {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
flex-direction: column;
width: 500px;
}
.search-box {
display: flex;
justify-content: start;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
table {
border: 1px solid #333;
}
td {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}.cover{
position: fixed;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
}
.content{
width: 500px;
margin: 200px auto;
background-color: white;
}
.title{
padding: 30px;
border-bottom: 1px solid black;
}.cover{
position: fixed;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
}
.content{
width: 500px;
margin: 200px auto;
background-color: white;
}
.title{
padding: 30px;
border-bottom: 1px solid black;
}11-ref 和 context
ref
ref 用于获取真实 dom,和 vue 中的 ref 一样
注意事项:
- ref 必须在挂载后获取,通常在 componentDidMount
- ref 获取组件,不能获取函数组件(获取函数组件不常见?需要获取怎么办?)
// ...
const refSon = React.createRef();
//..
<Son ref="refSon"></Son>;
//..// ...
const refSon = React.createRef();
//..
<Son ref="refSon"></Son>;
//..context
类似于 vue 的 provider 和 injected,用于嵌套多层的爷孙组件之间传值
注意事项:
- 子组件使用父组件创建的 context 对象,不能自己创建
- 只能传递一个 value 值,需要传多个属性,传个对象即可
/**
* React.createContext()
* 用于深层嵌套爷孙组件传值
* 创建导出,给子组件引入使用
*/
export const context1 = React.createContext();
//..
state = {
info: {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
},
};
//..
<context1.Provider value={this.state.info}>
<Son ref={refSon}></Son>
</context1.Provider>;
//../**
* React.createContext()
* 用于深层嵌套爷孙组件传值
* 创建导出,给子组件引入使用
*/
export const context1 = React.createContext();
//..
state = {
info: {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
},
};
//..
<context1.Provider value={this.state.info}>
<Son ref={refSon}></Son>
</context1.Provider>;
//..// ..
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
// ..
render() {
return <>
{/* 使用 */}
<context1.Consumer>
{(value) => {
return (
<div style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "center" }}>
<div>{value.name}</div>
<div>{value.age}岁</div>
</div>
);
}}
</context1.Consumer>
</>
}
// ..// ..
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
// ..
render() {
return <>
{/* 使用 */}
<context1.Consumer>
{(value) => {
return (
<div style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "center" }}>
<div>{value.name}</div>
<div>{value.age}岁</div>
</div>
);
}}
</context1.Consumer>
</>
}
// ..Example
import React from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
/**
* React.createRef()
* 用于获取真实dom和子组件信息
*/
const refDiv1 = React.createRef();
const refSon = React.createRef();
/**
* React.createContext()
* 用于深层嵌套爷孙组件传值
* 创建导出,给子组件引入使用
*/
export const context1 = React.createContext();
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
info: {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
},
};
componentDidMount() {
// console.log(this.refs.refSon); // 旧写法,严格模式下会提示报红
// console.log(refDiv1.current, refSon.current);
}
render() {
return (
<>
{/* <div className="app" ref={refDiv1}></div> */}
<Son ref="refSon"></Son>
<context1.Provider value={this.state.info}>
<Son ref={refSon}></Son>
</context1.Provider>
</>
);
}
}
export default App;import React from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
/**
* React.createRef()
* 用于获取真实dom和子组件信息
*/
const refDiv1 = React.createRef();
const refSon = React.createRef();
/**
* React.createContext()
* 用于深层嵌套爷孙组件传值
* 创建导出,给子组件引入使用
*/
export const context1 = React.createContext();
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
info: {
name: "王花花",
age: 18,
},
};
componentDidMount() {
// console.log(this.refs.refSon); // 旧写法,严格模式下会提示报红
// console.log(refDiv1.current, refSon.current);
}
render() {
return (
<>
{/* <div className="app" ref={refDiv1}></div> */}
<Son ref="refSon"></Son>
<context1.Provider value={this.state.info}>
<Son ref={refSon}></Son>
</context1.Provider>
</>
);
}
}
export default App;import React from "react";
import GrandSon from "./GrandSon";
class Son extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div>
子组件
<GrandSon></GrandSon>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;import React from "react";
import GrandSon from "./GrandSon";
class Son extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
render() {
return (
<div>
子组件
<GrandSon></GrandSon>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Son;import React from "react";
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
class GrandSon extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
componentDidMount() {
console.log(context1.Consumer);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
孙组件
{/* 使用 */}
<context1.Consumer>
{(value) => {
return (
<div style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "center" }}>
<div>{value.name}</div>
<div>{value.age}岁</div>
</div>
);
}}
</context1.Consumer>
</div>
);
}
}
export default GrandSon;import React from "react";
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
class GrandSon extends React.PureComponent {
state = {};
componentDidMount() {
console.log(context1.Consumer);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
孙组件
{/* 使用 */}
<context1.Consumer>
{(value) => {
return (
<div style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "center" }}>
<div>{value.name}</div>
<div>{value.age}岁</div>
</div>
);
}}
</context1.Consumer>
</div>
);
}
}
export default GrandSon;总结
- 通过 React.createRef(),给子组件绑定对应 ref 值
- Provider 与 Vue 不同,是使用 React.createContext()创建的值,并设置导出
- 创建:通过
<context.Provider value=data>标签包裹、标签内绑定值形式传值, - 使用:孙组件引入导出的 React.createContext,通过
<context.Consumer>{(value) => {}}<context.Consumer>
12-函数组件和 Hook
与 class 组件有什么区别
- 没有生命周期
- 没有 this
- 借助 Hook 完成各系列操作
- 函数组件本身相当于 render 函数
- props 在函数的第一个参数接收
state 的创建和更新
通过 useState 定义,返回数组包含两项,第一项是值、第二项是修改值的方法
const [value, setValue] = useState("hello");
// 使用
console.log(value);
// 修改
setValue("你好");const [value, setValue] = useState("hello");
// 使用
console.log(value);
// 修改
setValue("你好");useEffect 的使用
- 可以充当 componentDidMount、watch 监听
- 第一个参数为回调函数、第二参数只能是数组 -在数组中写入定义的 state 值,即可起到监听作用在
- useEffect 监听某个数据时,一开始渲染会执行一次(didMount),这点不同于 vue
- 引用内存地址改变时,监听才生效
const [value, setValue] = useState("hello");
useEffect(() => {
console.log("effect");
}, [value]);const [value, setValue] = useState("hello");
useEffect(() => {
console.log("effect");
}, [value]);useMemo
让一段计算在开始执行一次,后续只有依赖的数据发生变化时才重新运算
作用:
- 起类似于 vue 的一个计算属性的效果
- 缓存一个数据,让其不重新创建
const [arr, setArr] = useState([1, 2, 3]);
// 缓存,避免重新渲染时再次运行,起到优化作用
// 第一个参数也是必传,第二参数为数组[监听的数据],引用内存地址改变时,监听才生效
const all = useMemo(() => {
console.log("useMemo");
let _all = 0;
arr.forEach((item) => {
_all += item;
});
return _all;
}, [arr]);
setArr([...arr]); // 重新运行useMemo的第一个参数回函函数const [arr, setArr] = useState([1, 2, 3]);
// 缓存,避免重新渲染时再次运行,起到优化作用
// 第一个参数也是必传,第二参数为数组[监听的数据],引用内存地址改变时,监听才生效
const all = useMemo(() => {
console.log("useMemo");
let _all = 0;
arr.forEach((item) => {
_all += item;
});
return _all;
}, [arr]);
setArr([...arr]); // 重新运行useMemo的第一个参数回函函数useCallback
函数组件深层嵌套
export const context1 = React.createContext();
//..
{
/* 嵌套传值 */
}
<context1.Provider value="context value">
<Son></Son>
</context1.Provider>;
//..export const context1 = React.createContext();
//..
{
/* 嵌套传值 */
}
<context1.Provider value="context value">
<Son></Son>
</context1.Provider>;
//..import { useContext } from "react";
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
function Son() {
let contextValue = useContext(context1); // 使用useContext接收并返回
return <div>Provider: {contextValue}</div>;
}import { useContext } from "react";
import { context1 } from "./App"; // 引入
function Son() {
let contextValue = useContext(context1); // 使用useContext接收并返回
return <div>Provider: {contextValue}</div>;
}总结
- 使用 useState()返回一个 state 数据和修改对应 state 的方法
- useEffect 是指 state 更新时的副作用函数,可以充当 componentDidMount、vue-watch 作用
- useMemo 起到 vue-computed 作用,缓存-在某个数据更新时才执行回调函数
- useCallback 避免组件方法重新执行时再次创建方法
- useMemo、useCallback 都有优化性能作用,第二个参数必须得传[]
- useRef 获取真实 dom
- useContext(React.Provider()) 函数组件深层嵌套传值的使用方式,在父组件定义与 class 类组件的使用方式一样,只不过在子组件使用要借助 useContext(xxx)接收父组件暴露的值并返回 value
- 由于组件更新,会重新运行组件方法,会重新创建里面的属性、方法,避免重新创建方法,至于为什么后续性能优化会讲解
13-高阶组件
方法接收一个组件并返回一个匿名组件,这个返回结果成为高阶组件。高阶组件主要用于单纯的逻辑复用,不涉及 ui。
类似于 vue-Mixin 和自定义指令
基本使用
- 创建一个 TestHoc 文件,定义高阶组件函数,导出一个方法
import React from "react";
// 本质是一个方法,接收一个组件,返回一个匿名组件
function TestHoc(UserCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "hello hoc",
};
render() {
return (
<>
{/* props原封不动,其他数据、逻辑运算结果等可复用 */}
<UserCom msg={this.state.msg} {...this.props}></UserCom>
</>
);
}
};
}
export default TestHoc;import React from "react";
// 本质是一个方法,接收一个组件,返回一个匿名组件
function TestHoc(UserCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = {
msg: "hello hoc",
};
render() {
return (
<>
{/* props原封不动,其他数据、逻辑运算结果等可复用 */}
<UserCom msg={this.state.msg} {...this.props}></UserCom>
</>
);
}
};
}
export default TestHoc;- 导入使用,调用高阶组件函数传入需要复用逻辑的组件
import { useState } from "react";
// 1.引入
import TestHoc from "./TestHoc";
import Son from "./Son";
// 2.创建
const HocSon = TestHoc(Son);
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("王花花");
function handleChangeName() {
setName("李明花");
}
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
<button onClick={handleChangeName}>修改名称</button>
{/* 3.使用 */}
<HocSon name={name}></HocSon>
</div>
);
}
export default App;import { useState } from "react";
// 1.引入
import TestHoc from "./TestHoc";
import Son from "./Son";
// 2.创建
const HocSon = TestHoc(Son);
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("王花花");
function handleChangeName() {
setName("李明花");
}
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
<button onClick={handleChangeName}>修改名称</button>
{/* 3.使用 */}
<HocSon name={name}></HocSon>
</div>
);
}
export default App;例子说明
- 提供复用的数据和方法,给到组件 props,可以将很多页面都有的一些逻辑操作提取出来,写成高阶组件函数
- 提供生命周期,因为我们返回的是一个类组件,也可以使用 PureComponent,形成一个高阶的 PureComponent 组件
Ex: 获取鼠标在屏幕上的位置
import React from "react";
function TestHoc(UserCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
// 监听获取x,y
window.addEventListener("mousemove", (e) => {
const _x = e.clientX;
const _y = e.clientY;
this.setState({
x: _x,
y: _y,
});
});
}
render() {
return (
<>
{/* props传入x,y */}
<UserCom x={this.state.x} y={this.state.y} {...this.props}></UserCom>
</>
);
}
};
}
export default TestHoc;import React from "react";
function TestHoc(UserCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
// 监听获取x,y
window.addEventListener("mousemove", (e) => {
const _x = e.clientX;
const _y = e.clientY;
this.setState({
x: _x,
y: _y,
});
});
}
render() {
return (
<>
{/* props传入x,y */}
<UserCom x={this.state.x} y={this.state.y} {...this.props}></UserCom>
</>
);
}
};
}
export default TestHoc;import Son from "./Son";
import GetXYHoc from "./GetXYHoc";
const HocSon = GetXYHoc(Son); // 1.创建
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
{/* 2.使用 */}
<HocSon></HocSon>
</div>
);
}
export default App;import Son from "./Son";
import GetXYHoc from "./GetXYHoc";
const HocSon = GetXYHoc(Son); // 1.创建
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
{/* 2.使用 */}
<HocSon></HocSon>
</div>
);
}
export default App;function Son(props) {
return (
<div>
{/* 使用props获取x,y */}
x: {props.x},y: {props.y}
</div>
);
}
export default Son;function Son(props) {
return (
<div>
{/* 使用props获取x,y */}
x: {props.x},y: {props.y}
</div>
);
}
export default Son;Ex: 与 PureComponent 一样作用的高阶组件
import React from "react";
export default function MemoHoc(UseCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(props, state) {
let isShouldUpdate = false;
// 判断props
for (const key in this.props) {
if (this.props[key] !== props[key]) {
return (isShouldUpdate = true);
}
}
// 判断state
for (const key in this.state) {
if (this.state[key] !== state[key]) {
return (isShouldUpdate = true);
}
}
return isShouldUpdate;
}
render() {
return (
<>
<UseCom {...this.props}></UseCom>
</>
);
}
};
}import React from "react";
export default function MemoHoc(UseCom) {
return class extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(props, state) {
let isShouldUpdate = false;
// 判断props
for (const key in this.props) {
if (this.props[key] !== props[key]) {
return (isShouldUpdate = true);
}
}
// 判断state
for (const key in this.state) {
if (this.state[key] !== state[key]) {
return (isShouldUpdate = true);
}
}
return isShouldUpdate;
}
render() {
return (
<>
<UseCom {...this.props}></UseCom>
</>
);
}
};
}import { useState } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
import MemoHoc from "./MemoHoc";
const MemoSon = MemoHoc(Son);
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("王花花");
const [age, setAge] = useState(18);
function handleChangeName() {
setName("李明花");
}
function handleChangeAge() {
setAge(20);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
{/* 修改传入props值,会触发Son更新 */}
<button onClick={handleChangeName}>修改名称</button>
<MemoSon name={name}></MemoSon>
{/* 只修改state值,没有传入props,不会触发Son更新 */}
<button onClick={handleChangeAge}>修改年龄</button>
{age}岁
</div>
);
}
export default App;import { useState } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
import MemoHoc from "./MemoHoc";
const MemoSon = MemoHoc(Son);
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("王花花");
const [age, setAge] = useState(18);
function handleChangeName() {
setName("李明花");
}
function handleChangeAge() {
setAge(20);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>高阶组件</h1>
{/* 修改传入props值,会触发Son更新 */}
<button onClick={handleChangeName}>修改名称</button>
<MemoSon name={name}></MemoSon>
{/* 只修改state值,没有传入props,不会触发Son更新 */}
<button onClick={handleChangeAge}>修改年龄</button>
{age}岁
</div>
);
}
export default App;总结
- 组件:包含 ui 复用、逻辑复用
- 高阶组件:只复用操作逻辑、运算
类似于 vue 中的 Mixin 的用途,当我们发现某个逻辑操作或者某个运算在经常出现的时候,即可使用高阶组件。
“高阶函数”指函数接收一个方法返回一个新方法,高阶组件即使用函数接收一个组件返回一个新组件
14-React 性能和优化
react 的时间切片
Vue 有依赖收集,做到最小的更新范围,而 React 没有做这件事,而是整个组件树一块更新,就会有很长的 Diff 算法对比和计算工作。
这大量的更新,Diff 算法计算工作会耗大量时间,可能会阻塞主线程从而导致页面长时间白屏。
React 为了解决这个问题,选择使用一种策略-时间切片,也就是先计算一部分更新,然后让渡给浏览器主线程渲染,然后再进行下一步更新。以此往复。就不会出现上时间白屏了。
fiber
为了支持这种切片,我们需要把更新化成一个个单元,然后我们也必须有恢复上一次计算进度的能力
所以 react 设计了一种数据结构 fiber
把每个组件转化为一个 fiber 结构的对象,组成一个个单元。每个 Fiber 包含了三个指针,指向父节点、兄弟节点、子节点,这些指向让时间切片有了恢复上次中断的计算进度的能力。
性能保障
注意两点:层级组件联动更新、组件自身更新
1.避免父组件更新导致子组件更新
这是消耗性能最大的问题,类组件使用 PureComponent、函数组件使用 React.memo()
import React, { useState, useMemo, useCallback } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
// 使用React.memo包一层,作用避免子组件更新(React.memo本身就是一个高阶组件)
const MemoSon = React.memo(Son);
export default function App() {
let [num, setNum] = useState(0);
function handleChangeNum() {
let _num = num + 1;
setNum(_num);
}
return (
<div>
{num}
<button onClick={handleChangeNum}>修改</button>
<Son></Son>
<MemoSon></MemoSon>
</div>
);
}import React, { useState, useMemo, useCallback } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
// 使用React.memo包一层,作用避免子组件更新(React.memo本身就是一个高阶组件)
const MemoSon = React.memo(Son);
export default function App() {
let [num, setNum] = useState(0);
function handleChangeNum() {
let _num = num + 1;
setNum(_num);
}
return (
<div>
{num}
<button onClick={handleChangeNum}>修改</button>
<Son></Son>
<MemoSon></MemoSon>
</div>
);
}并非使用了 PureComponent 或 useMemo 就万事大吉,对于定义的非 state 数据,像一些写是的对象、方法并传给子组件 props,也会触发子组件更新
使用 useMemo 包裹对象、 useCallback 包裹方法来避免
import React, { useState, useMemo, useCallback } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
// 使用React.memo包一层,作用避免子组件更新(React.memo本身就是一个高阶组件)
const MemoSon = React.memo(Son);
export default function App() {
let [num, setNum] = useState(0);
const obj = {
a: 1,
};
function f1() {
console.log("f1");
}
// 使用 useMemo 对象, 第二参数必须传[]
const obj = useMemo(() => {
return { a: 1 };
}, []);
// 使用 useCallback 包裹 方法, 第二参数必须传[]
const f1 = useCallback(function () {
console.log("f1");
}, []);
function handleChangeNum() {
let _num = num + 1;
setNum(_num);
}
return (
<div>
{num}
<button onClick={handleChangeNum}>修改</button>
{/* <Son></Son> */}
<MemoSon></MemoSon>;
<MemoSon obj={obj} f1={f1}></MemoSon>;
</div>
);
}import React, { useState, useMemo, useCallback } from "react";
import Son from "./Son";
// 使用React.memo包一层,作用避免子组件更新(React.memo本身就是一个高阶组件)
const MemoSon = React.memo(Son);
export default function App() {
let [num, setNum] = useState(0);
const obj = {
a: 1,
};
function f1() {
console.log("f1");
}
// 使用 useMemo 对象, 第二参数必须传[]
const obj = useMemo(() => {
return { a: 1 };
}, []);
// 使用 useCallback 包裹 方法, 第二参数必须传[]
const f1 = useCallback(function () {
console.log("f1");
}, []);
function handleChangeNum() {
let _num = num + 1;
setNum(_num);
}
return (
<div>
{num}
<button onClick={handleChangeNum}>修改</button>
{/* <Son></Son> */}
<MemoSon></MemoSon>;
<MemoSon obj={obj} f1={f1}></MemoSon>;
</div>
);
}2.避免 state 同样的值产生更新
避免 state 修改为同样的值,而产生无意义的更新(类组件使用 PureComponent、函数组件使用 useState 定义本身就会判断)
总结
由于 react 更新是整个组件树更新,Diff 算法运算时间长,长了会导致阻塞浏览器渲染主线程,为了避免阻塞,react 设计了一种 fiber 数据结构,利用每段时间切片(16ms)空闲时间,以 fiber 单位,一个一个地更新,时间一到就中断交给主线程,该结构主要包含三个指向父节点、兄弟节点、子节点,避免恢复上一次中断的计算。
注意两点:层级组件联动更新、组件自身更新
- 避免父组件更新导致子组件更新
- PureComponent、函数组件 React.memo()
- 避免 state 同样的值产生更新
- PureComponent、函数组件使用 useState 定义本身就会判断
对于定义的非 state 数据,像一些写是的对象、方法并传给子组件 props,也会触发子组件更新 ,使用 useMemo 包裹对象、 useCallback 包裹方法来避免
15-react-router 的使用
React-router 三种版本
React-router 服务端渲染使用
React-router-dom 浏览器端渲染使用
React-router-native RN 混合开发
React-router 的使用步骤
- 通过 BroserRouter 或者 HashRouter 包裹组件
- 使用 Routes 组件,定义路由显示区域
- 使用 Route 组件,定义具体路由规则
- 使用 NavLink 或者 Link 组件,定义跳转链接
React-router 提供的一些其他重要组件
- Navigate 路由重定向
- Outlet,嵌套路由的子路由显示处
- 在父组件下引入 Outlet,提供子组件显示位置
- 子路由只需在 route 中嵌套即可,注意会自动拼接父路径+/子 path
import React from "react";
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route, NavLink } from "react-router-dom";
import Page2 from "./Page2";
import Page2Son1 from "./Page2Son1";
import Page2Son2 from "./Page2Son2";
function App() {
return (
<div className="name">
<BrowserRouter>
<NavLink to={"/Page2"}>Page2</NavLink>
<NavLink to={"/Page2/son1"}>Page2Son1</NavLink>
<NavLink to={"/Page2/son2"}>Page2Son2</NavLink>
<Routes>
{/* 嵌套路由 */}
<Route path="/Page2" element={<Page2 />}>
<Route path="son1" element={<Page2Son1 />}></Route>
<Route path="son2" element={<Page2Son2 />}></Route>
</Route>
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
</div>
);
}
export default App;import React from "react";
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route, NavLink } from "react-router-dom";
import Page2 from "./Page2";
import Page2Son1 from "./Page2Son1";
import Page2Son2 from "./Page2Son2";
function App() {
return (
<div className="name">
<BrowserRouter>
<NavLink to={"/Page2"}>Page2</NavLink>
<NavLink to={"/Page2/son1"}>Page2Son1</NavLink>
<NavLink to={"/Page2/son2"}>Page2Son2</NavLink>
<Routes>
{/* 嵌套路由 */}
<Route path="/Page2" element={<Page2 />}>
<Route path="son1" element={<Page2Son1 />}></Route>
<Route path="son2" element={<Page2Son2 />}></Route>
</Route>
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
</div>
);
}
export default App;import React from "react";
import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom"; // 引入
export default function Page2() {
return (
<div>
Page2
{/* 使用 */}
<Outlet></Outlet>
</div>
);
}import React from "react";
import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom"; // 引入
export default function Page2() {
return (
<div>
Page2
{/* 使用 */}
<Outlet></Outlet>
</div>
);
}如何获取路由参数
- Params 参数
- v6:useParams
- v5:this.props.match.params
import { useSearchParams } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page4() {
// 2.解构
let [searchParams, setSearchParams] = useSearchParams();
// 3.通过searchParams原型上的get方法获取
console.log(searchParams.get("a"));
return (
<div>
Page4
{/* 4.通过setSearchParams方法修改 */}
<button
onClick={() => {
setSearchParams({
a: 123,
b: 456,
});
}}
>
修改路由参数
</button>
</div>
);
}import { useSearchParams } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page4() {
// 2.解构
let [searchParams, setSearchParams] = useSearchParams();
// 3.通过searchParams原型上的get方法获取
console.log(searchParams.get("a"));
return (
<div>
Page4
{/* 4.通过setSearchParams方法修改 */}
<button
onClick={() => {
setSearchParams({
a: 123,
b: 456,
});
}}
>
修改路由参数
</button>
</div>
);
}- Query 参数
- v6:useSearchParams
- v5:this.props.location.search
//
<Route path="/Page3/:id" element={<Page3 />}></Route>;
//
// query - /page2/99
import { useParams } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page3() {
// 2.获取
let routerParams = useParams();
console.log(routerParams); // {id: 99}
return <div>Page3</div>;
}//
<Route path="/Page3/:id" element={<Page3 />}></Route>;
//
// query - /page2/99
import { useParams } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page3() {
// 2.获取
let routerParams = useParams();
console.log(routerParams); // {id: 99}
return <div>Page3</div>;
}- Location 信息
- v6: useLocation
- v5: this.props.location.state
import { useLocation } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page1() {
console.log(useLocation()); // 2.获取
return <div>Page1</div>;
}import { useLocation } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page1() {
console.log(useLocation()); // 2.获取
return <div>Page1</div>;
}通过 js 跳转路由
- v6: useNavigate 创建跳转方法
- v5: this.props.history.push()
import { Outlet, useNavigate } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page2() {
// 2.获取
let navTo = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
Page2
<button
onClick={() => {
{
/* 3.使用 */
}
navTo("/Page1", {
// state也是一种参数,可在useLocation返回的对象中获取,但不在url显示
state: {
state1: "hello",
},
});
}}
>
跳转到page1
</button>
<Outlet></Outlet>
</div>
);
}import { Outlet, useNavigate } from "react-router-dom"; // 1.引入
export default function Page2() {
// 2.获取
let navTo = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
Page2
<button
onClick={() => {
{
/* 3.使用 */
}
navTo("/Page1", {
// state也是一种参数,可在useLocation返回的对象中获取,但不在url显示
state: {
state1: "hello",
},
});
}}
>
跳转到page1
</button>
<Outlet></Outlet>
</div>
);
}路由鉴权
// ...
const _token = localStorage.getItem("token");
// ...
// 不渲染
{
_token ? <Route path="/Page1" element={<Page1 />}></Route> : "";
}
// 重定向
<Route path="/Page1" element={_token ? <Page1 /> : <Navigate to="/Page4"></Navigate>}></Route>;// ...
const _token = localStorage.getItem("token");
// ...
// 不渲染
{
_token ? <Route path="/Page1" element={<Page1 />}></Route> : "";
}
// 重定向
<Route path="/Page1" element={_token ? <Page1 /> : <Navigate to="/Page4"></Navigate>}></Route>;异步路由
react 做异步路由,需要配合 react 本身的 lazy 方法和 suspense 组件
import { lazy, Suspense } from "react";
let LazyPage4 = lazy(() => {
return import("./Page4");
});
// ..
/* Suspense作用:过渡效果,组件还没加载好显示加载中 */
<Suspense fallback={<h1>加载中</h1>}>
<Routes>
<Route path="/Page4" element={<LazyPage4 />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Suspense>;
// ...import { lazy, Suspense } from "react";
let LazyPage4 = lazy(() => {
return import("./Page4");
});
// ..
/* Suspense作用:过渡效果,组件还没加载好显示加载中 */
<Suspense fallback={<h1>加载中</h1>}>
<Routes>
<Route path="/Page4" element={<LazyPage4 />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Suspense>;
// ...感受 React 的全局插件使用方式
react 中没有 vue 那样的 vue.use 方法,react 中使用一个插件,库,都是引入一个组件,然后把要使用该插件的部分包裹起来。
总结
- react 路由有三个版本,主要使用 react-router-dom 版本,该版本 v5 和 v6 使用上有很大区别(类和 Hook)
- 两种路由模式,使用 BrowserRouter 或者 HashRouter 包裹 App
- 使用 Routes + Route 定义路由规则, Route 两个 props 值,path 路劲,element 组件
- 嵌套子路由只需在 Route 中嵌套 Route,会自动拼接父级组件路径+/子路由 path 路径
- 携带\获取参数
- query 只需在定义路由规则 path="page1/:id", 子组件中调用 useParams()获取
- params 麻烦一点,结构 useSearchParams() => [searchParams, setSearchParams],通过 searchParams.get('x')获取、setSearchParams({a:'1'})设置
- location 通过 useLocation()即可获取,setSearchParams({a:'1'},state({这里也能设置值}))
- 路由鉴权,判断 localStorage.getItem("token");
16-react 中的全局状态管理
react 没有想 vue 一样有个专门处理全局状态值的库 vuex,只是依赖普通的 js 状态管理库,主要用的有:
- 最老的是 redux
- 新的 mobx
先说 redux
安装依赖
npm install redux @redux/toolkitnpm install redux @redux/toolkit创建 store
// store/index.js
// 新版本方法名legacy_createStore
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from "redux"; // 1.引入
// 2.定义方法
function mesReducer(state = { mes: "hello" }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "changeMes":
state.mes = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetMes":
state.mes = "hello";
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 3.创建store
let store = createStore(mesReducer);
export default store;// store/index.js
// 新版本方法名legacy_createStore
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from "redux"; // 1.引入
// 2.定义方法
function mesReducer(state = { mes: "hello" }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "changeMes":
state.mes = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetMes":
state.mes = "hello";
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 3.创建store
let store = createStore(mesReducer);
export default store;项目中使用
// App.js
import store from "../../store/index";
let state = store.getState();
//..
<div>mes:{state.mes}</div>;
<button onClick={() => {
store.dispatch({
type: 'changeMes',
payload: "hello word!"
})
console.log(store.getState());
}}>修改mes</button>
}
//...// App.js
import store from "../../store/index";
let state = store.getState();
//..
<div>mes:{state.mes}</div>;
<button onClick={() => {
store.dispatch({
type: 'changeMes',
payload: "hello word!"
})
console.log(store.getState());
}}>修改mes</button>
}
//...由于只是普通 js 库,跟 react 没有关联,修改值后但是不能使 react 组件更新,可通过监听 store 的改变,调用 render,不过这种方式过于简单粗暴
store.subscribe(() => {
render(root);
});store.subscribe(() => {
render(root);
});使用 react-redux 的 Provider 和 connect
- 安装
npm install react-reduxnpm install react-redux- 使用
- 使用 Provider 包裹 App,并传将 store 作为 props 传递
// index.js
import store from "./store/index";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
//...
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>;
//...// index.js
import store from "./store/index";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
//...
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>;
//...- 使用 connect 包裹导出的组件,定义映射的 state 到 props,自定义修改对应 state 方法
import { connect } from "react-redux";
function App(props) {
console.log(props);
return (
<div className="container">
redux
<div>mes:{props.mes}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
props.changeMes();
}}
>
修改mes
</button>
</div>
);
}
/**
* 第一个参数是将哪些属性 映射到props,必须返回一个对象
* 第二个参数是方法映射,给props里加入哪些方法,没有传就用props.dispatch
*/
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
return {
mes: state.mes,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);
export default reduxApp;import { connect } from "react-redux";
function App(props) {
console.log(props);
return (
<div className="container">
redux
<div>mes:{props.mes}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
props.changeMes();
}}
>
修改mes
</button>
</div>
);
}
/**
* 第一个参数是将哪些属性 映射到props,必须返回一个对象
* 第二个参数是方法映射,给props里加入哪些方法,没有传就用props.dispatch
*/
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
return {
mes: state.mes,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);
export default reduxApp;多模块
- 从 react-redux 引入 combineReducers
- 定义另外 reducer 方法
- 将新定义的 reducer 以对象形式传入 combineReducers()
- 将 combineReducers({...})结果传入 createStore(...)
- 使用 state 需要前面加模块名称,dispatch 修改不用
// 1. 引入
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from "redux";
import { legacy_createStore as createStore, combineReducers } from "redux";
// 2.定义
function mesReducer(state = { mes: "hello" }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "changeMes":
state.mes = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetMes":
state.mes = "hello";
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
function numReducer(state = { num: 0 }, action) {
switch (
action.type
) {
case "changeNum":
state.num = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetNum":
state.num = 99;
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 3.传入 combineReducers
let reducer = combineReducers({
mesReducer,
numReducer,
});
// 4.创建多模块仓库
let store = createStore(mesReducer);
let store = createStore(reducer);
export default store;// 1. 引入
import { legacy_createStore as createStore } from "redux";
import { legacy_createStore as createStore, combineReducers } from "redux";
// 2.定义
function mesReducer(state = { mes: "hello" }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "changeMes":
state.mes = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetMes":
state.mes = "hello";
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
function numReducer(state = { num: 0 }, action) {
switch (
action.type
) {
case "changeNum":
state.num = action.payload;
return { ...state };
case "resetNum":
state.num = 99;
return { ...state };
default:
return state;
}
}
// 3.传入 combineReducers
let reducer = combineReducers({
mesReducer,
numReducer,
});
// 4.创建多模块仓库
let store = createStore(mesReducer);
let store = createStore(reducer);
export default store;import { connect } from "react-redux";
function App(props) {
console.log(props);
return (
<div className="container">
redux
<div>mes:{props.mes}</div>
<div>num:{props.num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
props.changeMes();
}}
>
修改mes
</button>
</div>
);
}
/**
* 第一个参数是将哪些属性 映射到props,必须返回一个对象
* 第二个参数是方法映射,给props里加入哪些方法
*/
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);
export default reduxApp;import { connect } from "react-redux";
function App(props) {
console.log(props);
return (
<div className="container">
redux
<div>mes:{props.mes}</div>
<div>num:{props.num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
props.changeMes();
}}
>
修改mes
</button>
</div>
);
}
/**
* 第一个参数是将哪些属性 映射到props,必须返回一个对象
* 第二个参数是方法映射,给props里加入哪些方法
*/
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);
export default reduxApp;@reduxjs/toolkit
创建以及使用方式
// 1.引入
import { createSlice, configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
// 2.定义切片
let mesSlice = createSlice({
name: "mesSlice", // 切片名,dispatch时需要加的前缀
initialState: {
mes: "hello",
},
reducers: {
changeMes(state, action) {
state.mes = action.payload;
},
},
});
let numSlice = createSlice({
name: "numSlice",
initialState: {
num: 0,
},
reducers: {
addNum(state, action) {
state.num += 1;
},
},
});
// 3.配置模块化仓库
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
mesReducer: mesSlice.reducer,
numReducer: numSlice.reducer,
},
});
export default store;// 1.引入
import { createSlice, configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
// 2.定义切片
let mesSlice = createSlice({
name: "mesSlice", // 切片名,dispatch时需要加的前缀
initialState: {
mes: "hello",
},
reducers: {
changeMes(state, action) {
state.mes = action.payload;
},
},
});
let numSlice = createSlice({
name: "numSlice",
initialState: {
num: 0,
},
reducers: {
addNum(state, action) {
state.num += 1;
},
},
});
// 3.配置模块化仓库
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
mesReducer: mesSlice.reducer,
numReducer: numSlice.reducer,
},
});
export default store;// ...
// import store from "./store/index";
import store from "./store/toolkitIndex";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
// <React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
// </React.StrictMode>
);
/// ...// ...
// import store from "./store/index";
import store from "./store/toolkitIndex";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
// <React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
// </React.StrictMode>
);
/// ...let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); // 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "mesSlice/changeMes",
type: "mesSlice/changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); // 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
dispatch({
type: "mesSlice/changeMes",
type: "mesSlice/changeMes",
payload: "hello word!",
});
},
};
}
)(App);一般使用解构暴露形式去改变 state
//...
let mesSlice = createSlice({...})
let numSlice = createSlice({...});
// console.log(mesSlice.actions); // {changeMes: ƒ}
export let { changeMes } = mesSlice.actions
export let { addNum } = numSlice.actions
export default store;
//...//...
let mesSlice = createSlice({...})
let numSlice = createSlice({...});
// console.log(mesSlice.actions); // {changeMes: ƒ}
export let { changeMes } = mesSlice.actions
export let { addNum } = numSlice.actions
export default store;
//...// 1. 引入
import { changeMes, addNum } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
//..
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); // 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
// 2.传入
dispatch(changeMes("hello word"));
},
addNum() {
// 2.传入
dispatch(addNum());
},
};
}
)(App);
//..// 1. 引入
import { changeMes, addNum } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
//..
let reduxApp = connect(
(state) => {
console.log(state); // 模块结果{mesReducer: {…}, numReducer: {…}}
return {
mes: state.mesReducer.mes,
num: state.numReducer.num,
};
},
(dispatch) => {
return {
changeMes() {
// 2.传入
dispatch(changeMes("hello word"));
},
addNum() {
// 2.传入
dispatch(addNum());
},
};
}
)(App);
//..使用 hook 的方式
只能用于 toolkit,只能用于函数组件
// 1. 引入
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { addNum } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
function App2() {
// 2. 映射到state
let num = useSelector((state) => {
return state.numReducer.num;
});
let dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="container">
toolkit-hook
{/* 3.使用 */}
<div>num:{num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
//4.修改方式1
dispatch({
type: "numSlice/addNum",
});
// 4.修改方式2
dispatch(addNum());
}}
>
修改num
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App2;// 1. 引入
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { addNum } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
function App2() {
// 2. 映射到state
let num = useSelector((state) => {
return state.numReducer.num;
});
let dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="container">
toolkit-hook
{/* 3.使用 */}
<div>num:{num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
//4.修改方式1
dispatch({
type: "numSlice/addNum",
});
// 4.修改方式2
dispatch(addNum());
}}
>
修改num
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App2;异步问题!!
无论 react-redux 或 toolkit 中,异步都是需要特殊处理的,否则报错
使用 createAsyncThunk 创建并暴露出去,在对应切片中定义 extraReducers
// 1. 引入
import { createSlice, configureStore, createAsyncThunk } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
// 2. 定义thunk异步,定义必须在 slice 前面,第一个参数可随意起,第二个参数异步函数返回一个Promise
export let changeNumThunk = createAsyncThunk("numSlice/changeNum", async () => {
let res = await new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(999);
}, 1000);
});
return res;
});
// 3.切片中定义 extraReducers
let numSlice = createSlice({
name: "numSlice",
initialState: {
num: 0,
},
reducers: {
addNum(state, action) {
state.num += 1;
},
},
// 异步reducers
extraReducers: (chunk) => {
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.pending, () => {
console.log("pending");
});
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.num = action.payload;
});
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.rejected, () => {
console.log("rejected");
});
},
// 对象写法
// extraReducers: {
// [changeNumThunk.fulfilled]:(state, action) => {
// state.num = action.payload
// }
// }
});
// 3.配置模块化仓库
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
numReducer: numSlice.reducer,
},
});
// console.log(numSlice.actions); // {changeNum: ƒ}
export let { addNum } = numSlice.actions;
export default store;// 1. 引入
import { createSlice, configureStore, createAsyncThunk } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
// 2. 定义thunk异步,定义必须在 slice 前面,第一个参数可随意起,第二个参数异步函数返回一个Promise
export let changeNumThunk = createAsyncThunk("numSlice/changeNum", async () => {
let res = await new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(999);
}, 1000);
});
return res;
});
// 3.切片中定义 extraReducers
let numSlice = createSlice({
name: "numSlice",
initialState: {
num: 0,
},
reducers: {
addNum(state, action) {
state.num += 1;
},
},
// 异步reducers
extraReducers: (chunk) => {
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.pending, () => {
console.log("pending");
});
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.num = action.payload;
});
chunk.addCase(changeNumThunk.rejected, () => {
console.log("rejected");
});
},
// 对象写法
// extraReducers: {
// [changeNumThunk.fulfilled]:(state, action) => {
// state.num = action.payload
// }
// }
});
// 3.配置模块化仓库
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
numReducer: numSlice.reducer,
},
});
// console.log(numSlice.actions); // {changeNum: ƒ}
export let { addNum } = numSlice.actions;
export default store;import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { changeNumThunk } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
function App2() {
// hook是映射到state上
let num = useSelector((state) => {
return state.numReducer.num;
});
let dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="container">
toolkit-hook
<div>num:{num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
dispatch(changeNumThunk());
}}
>
异步修改
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App2;import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { changeNumThunk } from "../../store/toolkitIndex";
function App2() {
// hook是映射到state上
let num = useSelector((state) => {
return state.numReducer.num;
});
let dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="container">
toolkit-hook
<div>num:{num}</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
dispatch(changeNumThunk());
}}
>
异步修改
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App2;总结
- react 没有专用的状态管理库,像常用最老的 redux 都是普通 js 的库
- 普通 js 库不能触发 react 组件更新,使用 react-redux 库,本质是通过将 store 的值映射到 props,使用 Provider 包裹 App,并传将 store 作为 props 传递
- 多模块使用 combineReducers({...}),将 reducer 作为对象键值传入
- @reduxjs/toolkit,解决 redux 定义默认值、行为过于繁琐,提供更舒服的创建方式,基于 redux,不过它是将 state 映射到 state 中,而不是 props 了,还有一点,toolkit 支持以 hook 方式在函数组件中使用,提供了 useSelector, useDispatch
- 关于异步问题,redux、toolkit 是需要特殊处理的,使用 createAsyncThunk 接收两个参数,名称、异步函数返回一个 Promise, 创建并暴露出去,在对应切片中定义 extraReducers,处理不同状态(pending、fulfilled、rejected)时执行的回调函数。
17-react 中的路由权限控制
流程: 初始只有登录页面 - 获取用户页面权限 -把用户页面权限和初始路由合并 - 存储到 redux 中 - 触发 app 重新渲染 - 生成路由
- 初始只有登录页面
- 将初始(公共的路由)和权限路由分开,创建时合并用户页面权限路由
- 获取用户页面权限
- 接口获取用户权限,数据格式为树结构,包含组件标题、组件名等信息;也可以返回组件名字符串,但是需要本地去匹配。
- 以前面的方式,根据接口返回的路由数据结构和 component 字段递归创建路由
存储 redux 仓库中,在映射到组件state,数据更新时,组件也更新、重新生成路由
本地存储化,避免通过地址栏跳转、触发App和redux仓库初始化
import Page1 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page1";
import Page2 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2";
import Page3 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page3";
import Page2Son1 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2Son1";
import Page2Son2 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2Son2";
import Page4 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page4";
import Login from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Login";
export default {
Page1,
Page2,
Page3,
Page2Son1,
Page2Son2,
Page4,
Login,
};import Page1 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page1";
import Page2 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2";
import Page3 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page3";
import Page2Son1 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2Son1";
import Page2Son2 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page2Son2";
import Page4 from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Page4";
import Login from "../components/17-路由权限控制/Login";
export default {
Page1,
Page2,
Page3,
Page2Son1,
Page2Son2,
Page4,
Login,
};import { Route } from "react-router-dom";
import routeMap from "../router/routesMap";
// 递归创建路由,根据 component 字段匹配
export function createRoute(routesList) {
return routesList.map((item) => {
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
return (
<Route key={item.path} path={item.path} Component={routeMap[item.component]}>
{createRoute(item.children)}
</Route>
);
} else {
return <Route key={item.path} path={item.path} Component={routeMap[item.component]}></Route>;
}
});
}import { Route } from "react-router-dom";
import routeMap from "../router/routesMap";
// 递归创建路由,根据 component 字段匹配
export function createRoute(routesList) {
return routesList.map((item) => {
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
return (
<Route key={item.path} path={item.path} Component={routeMap[item.component]}>
{createRoute(item.children)}
</Route>
);
} else {
return <Route key={item.path} path={item.path} Component={routeMap[item.component]}></Route>;
}
});
}// 数据格式
const userInfo = {
name: "admin1",
routes: [
{
path: "/page1",
component: "Page1",
},
{
path: "/page2",
component: "Page2",
children: [
{
path: "page2Son",
component: "Page2Son",
},
{
path: "page2Son2",
component: "Page2Son2",
},
],
},
],
};// 数据格式
const userInfo = {
name: "admin1",
routes: [
{
path: "/page1",
component: "Page1",
},
{
path: "/page2",
component: "Page2",
children: [
{
path: "page2Son",
component: "Page2Son",
},
{
path: "page2Son2",
component: "Page2Son2",
},
],
},
],
};import { BrowserRouter, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import { createRoute } from "../../router/createRoute";
import origanRoutes from "../../router/routesList"; // 初始路由
import { useSelector } from "react-redux";
function App() {
// 获取仓库中的权限路由
let routesList = useSelector((state) => {
return state.userInfo.routes;
});
return (
<div>
<BrowserRouter>
{/* 创建时把用户页面权限路由跟初始路由合并 */}
<Routes>{createRoute(origanRoutes.concat(routesList))}</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
</div>
);
}
export default App;import { BrowserRouter, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import { createRoute } from "../../router/createRoute";
import origanRoutes from "../../router/routesList"; // 初始路由
import { useSelector } from "react-redux";
function App() {
// 获取仓库中的权限路由
let routesList = useSelector((state) => {
return state.userInfo.routes;
});
return (
<div>
<BrowserRouter>
{/* 创建时把用户页面权限路由跟初始路由合并 */}
<Routes>{createRoute(origanRoutes.concat(routesList))}</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
</div>
);
}
export default App;18-组件库等相关生态
 LinQiang·Shen
LinQiang·Shen